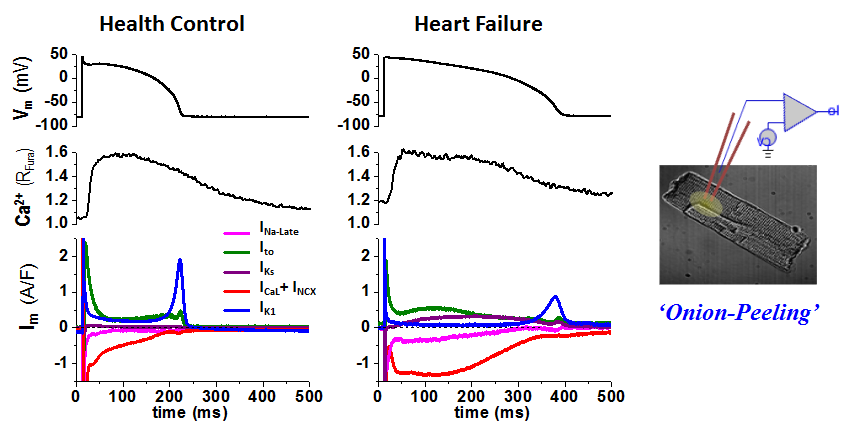
 We conduct state-of-the-art experiments to study the ion channels and action potentials that control cardiac electrophysiology. To study how theinward currents and the outward currents counterbalance in the same cell to shape the cell’s action potential, we developed an innovative AP-clamp Sequential Dissection (named Onion-Peeling) technique to record multiple ionic currents in the same single cell under AP-clamp. This presents a step forward from the previous V-clamp approach that measures only one current from any one cell, and provides a new tool to enable direct experimental measurements of changes in multiple ionic currents under various disease related conditions such as elevated CaMKII or ROS activation or hyper β-adrenergic stimulation. Using this new technique, we discovered that (a) there is cell-to-cell variability in the expression of ionic currents; (b) in healthy myocytes, the inward and the outward currents counterbalance to shape normal action potential profile; (c) however, under disease conditions the changes in different currents can go out of balance to cause arrhythmogenic actin potentials. We also studied the β-adrenergic effects on altering the major K+ channels that control cardiac repolarization — IKs, IKr, IK1 — and quantified the changes of these currents under physiological to pathological level of β-adrenergic stimulation and the relative contribution of each K+ channel to repolarization, pertaining to using specific blockers to treat LQT1 and LQT2 syndromes. Previously, such quantitative study was only possible in model simulations, the Onion-Peeling technique now enable direct experimental measurements, which can serve to refine models.
We conduct state-of-the-art experiments to study the ion channels and action potentials that control cardiac electrophysiology. To study how theinward currents and the outward currents counterbalance in the same cell to shape the cell’s action potential, we developed an innovative AP-clamp Sequential Dissection (named Onion-Peeling) technique to record multiple ionic currents in the same single cell under AP-clamp. This presents a step forward from the previous V-clamp approach that measures only one current from any one cell, and provides a new tool to enable direct experimental measurements of changes in multiple ionic currents under various disease related conditions such as elevated CaMKII or ROS activation or hyper β-adrenergic stimulation. Using this new technique, we discovered that (a) there is cell-to-cell variability in the expression of ionic currents; (b) in healthy myocytes, the inward and the outward currents counterbalance to shape normal action potential profile; (c) however, under disease conditions the changes in different currents can go out of balance to cause arrhythmogenic actin potentials. We also studied the β-adrenergic effects on altering the major K+ channels that control cardiac repolarization — IKs, IKr, IK1 — and quantified the changes of these currents under physiological to pathological level of β-adrenergic stimulation and the relative contribution of each K+ channel to repolarization, pertaining to using specific blockers to treat LQT1 and LQT2 syndromes. Previously, such quantitative study was only possible in model simulations, the Onion-Peeling technique now enable direct experimental measurements, which can serve to refine models.
Relevant Publications
- Banyasz T, Jian Z, Horvath B, Khabbaz S, Izu LT, Chen-Izu Y*. Beta-adrenergic stimulation reverses the IKr–IKs dominant pattern during cardiac action potential. Pflügers Archiv – European J Physiol. (2014) 466:2067–2076. PMID:24535581 PMC4138296
- Tamas Banyasz, Balazs Horvath, Zhong Jian, Leighton T. Izu and Chen-Izu Y*. Sequential dissection of multiple ionic currents in single cardiac myocytes under action potential-clamp. J Mol Cell Cardiology (2011) 50:578-581. PMC3047417
- Chen-Izu Y*. Multiple levels of the single L-type Ca2+ channel conductance in adult mammalian ventricular myocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 391(1):604-608 (2009). PMC2818605
- Chen-Izu Y, Sha Q, Shorofsky SR, Robinson SW, Wier WG, Goldman L, Balke CW*. ICa(TTX) channels are distinct from those generating the classical cardiac Na+ current Biophysical J 81:2647-2659 (2001). PMCID: MC1301732
- Chen-Izu Y*, Moreno AP, Spangler RA. Opposing gates model for voltage gating of gap junction channels. Am J Physiol. 281:C1604-C1613 (2001).
- Chen-Izu Y*, Xiao R-P*, Izu LT, Cheng H, Kuschul M, Spurgeon H, and Lakatta EG. Gi-dependent localization of β-adrenergic receptor signaling to L-type Ca2+ channels. Biophysical J 79:2547-2556 (2000). PMCID: PMC 1301137
